Eczema
What is Eczema
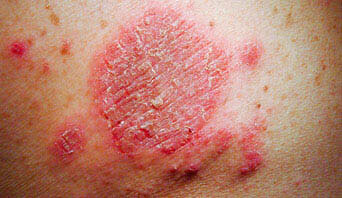
Eczema, also referred to as eczematous dermatitis, is a type of inflammation of the skin. Skin affected by eczema is often dry and cracked, the protective outer layer of skin damaged. As a result, skin affected by eczema loses a lot of water, which interferes with the natural healing process. Eczema is a common problem which can appear all over the body but it is not contagious.
Symptoms of Eczema

Eczema symptoms can be different for each person. The rash may look different on various parts of body. It can be mild, moderate, or severe. Symptoms of eczema include inflamed, dry, scaly, red, extremely itchy and swollen skin which sometimes includes fluid-filled bumps that ooze and crust. At times the itch may be so intense that patients will scratch their skin until it bleeds, leading to even more inflammation and itching. This is called the itch-scratch cycle.
Types and Causes of Eczema
Some of the most common types of Eczema include:
- Atopic Dermatitis: The most common type of dermatitis, affecting babies and young children is characterized by dry, red, raw patches of skin on the face, scalp, and inner elbow’s and/or behind the knees. Atopic dermatitis is hereditary and symptoms can present differently where in some people it may come and go or in others, remain present at all times.
- Allergic Contact Dermatitis: caused by a delayed immune reaction following skin contact with an allergic substance. Within 48 hours the skin will become inflamed. Poison Ivy, dyes, perfumes, and metals are among some of the most common causes.
- Irritant Contact Dermatitis: caused by repeat exposure to substances that chemically damage the skin, including harsh soaps, detergents and cleaning products. These irritants remove oil and moisture from the outer layer of the skin, damaging the protective layer and stimulating inflammation.
- Nummular Eczema: can occur at any age. It looks much different from the usual atopic dermatitis and can be much more difficult to treat. It is characterized by spots that appear “coin” shaped on the skin. They may be very itchy or not itchy at all. They can also be very dry and scaly or be wet and open. The cause of nummular eczema does not seem to be hereditary but is triggered by an event such as an insect bite, dry skin in the winter or a reaction to inflammation elsewhere on the body. Most individuals with this type of eczema seem to clear up completely after a short time and do not appear to have the long-term issues seen in other forms of eczema.
- Eczema on Hands: Hand eczema is a condition resulting from a combination of factors including genetics as well as contact with irritants and allergens such as chemicals. This type of eczema develops on the hands and is commonly job-related. It can be made worse with frequent hand washing and exposure to specific chemicals, often involved in cleaning, catering, mechanical and health care professions causing itchy, dry, scaly patches of skin that crack and flake.
How to Treat Eczema
Reduce the frequency of eczema “flare-ups” by following a few simple tips including;
- Reduce stress
- Avoiding scratchy materials, such as wool
- Avoid harsh soaps, detergents & chemicals
- Moisturize frequently, especially in cold weather
- Avoid sweating
- Choose cotton for bed linens & clothing
Eczema cannot be cured but proper diagnosis and treatment from a skin specialist is important to minimizing eczema’s impact. Dr. Patenaude can provide you with a treatment plan tailored to your eczema which may include eczema medication, eczema cream and/or other in-house treatments. If you are concerned that you may be suffering from eczema have your family doctor refer you to Dr. Patenaude for a medical assessment.





